Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
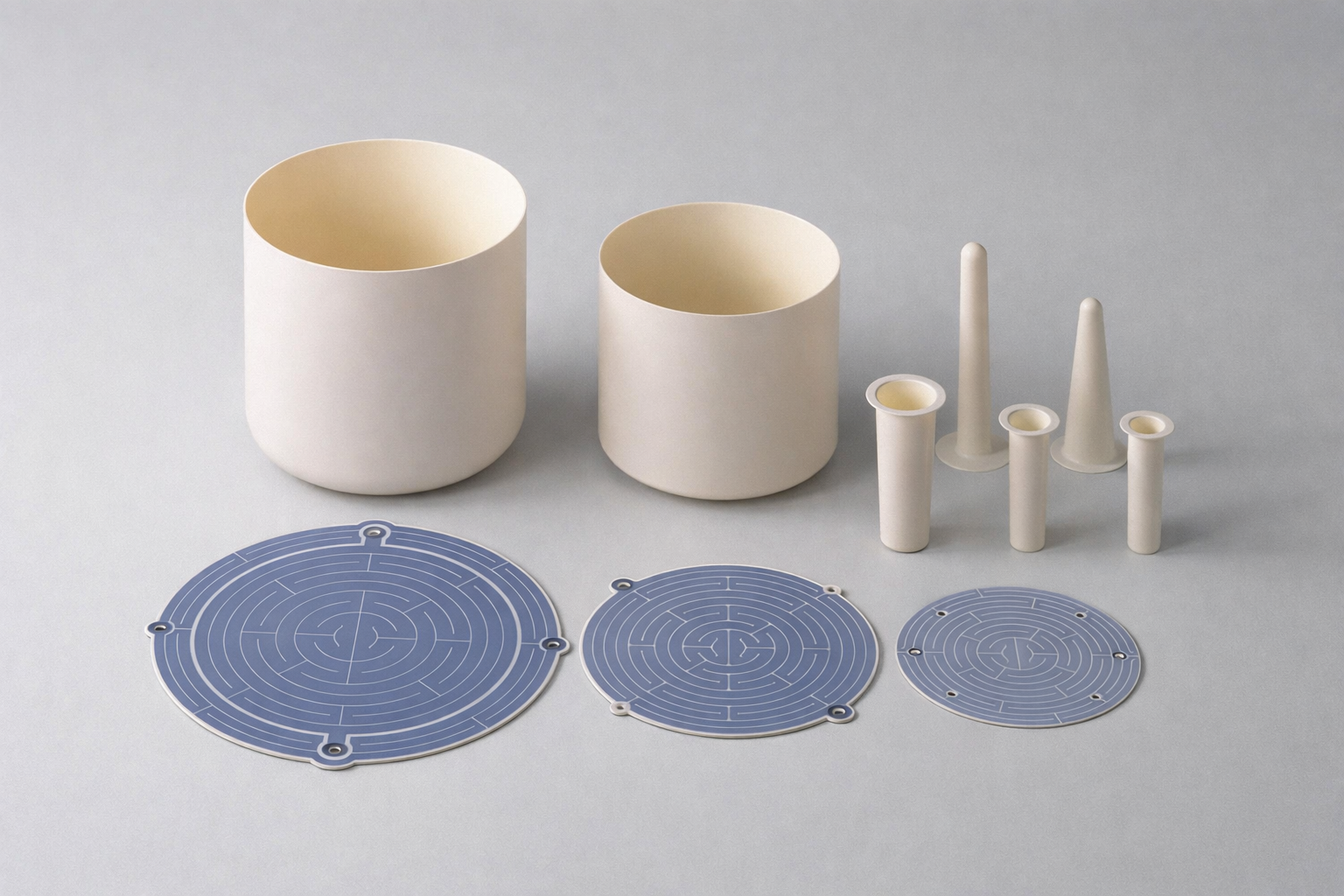
Introduction
Pyrolytic Boron Nitride (PBN) is a high-purity advanced ceramic manufactured exclusively by chemical vapor deposition (CVD). Unlike conventionally sintered or hot-pressed boron nitride, PBN is produced without any binders or sintering additives, resulting in a material with exceptional chemical cleanliness, structural uniformity, and performance reliability. These attributes make PBN a preferred material for semiconductor processing, crystal growth, and high-temperature vacuum systems, where contamination control and thermal stability are critical.
PBN is formed through the CVD deposition of boron- and nitrogen-containing gases onto a heated substrate. During deposition, boron nitride grows in a highly oriented, layered crystalline structure, similar to graphite. This structure leads to pronounced anisotropy in thermal and mechanical behavior, which can be engineered through precise control of deposition parameters such as temperature, gas flow, and growth rate.
The CVD process produces a fully dense, non-porous material with extremely low outgassing, making PBN inherently suitable for ultra-high vacuum environments.
PBN ceramics typically achieve a purity level of ≥99.99%, with minimal metallic and oxygen impurities. The absence of open porosity ensures excellent gas tightness, and helium leak rates can reach ~10⁻¹⁰ cm³/s, meeting the requirements of UHV systems used in semiconductor manufacturing and research equipment.
PBN exhibits outstanding thermal stability under extreme conditions. In vacuum or inert atmospheres, it can operate continuously at temperatures up to 1800–2000 °C. In oxidizing environments, PBN remains stable up to approximately 900 °C, beyond which oxidation gradually accelerates.
The material also shows excellent resistance to thermal cycling, maintaining dimensional stability during repeated heating and cooling processes.
Due to its layered crystal structure, PBN displays anisotropic thermal conductivity. Typical in-plane thermal conductivity values range from 60 to 120 W/(m·K), while through-thickness conductivity is significantly lower. This anisotropy contributes to superior thermal shock resistance, reducing the risk of cracking during rapid temperature changes.
PBN is an excellent electrical insulator, with room-temperature volume resistivity typically exceeding 10¹⁴ Ω·cm. Even at temperatures approaching 1000 °C, the resistivity remains above 10⁸ Ω·cm. Its dielectric constant is relatively low (approximately 3.5–4.0), with low dielectric loss, supporting stable performance in high-temperature electrical insulation applications.
PBN demonstrates strong chemical inertness toward most molten metals, semiconductors, and corrosive process environments. It exhibits non-wetting behavior with materials such as gallium, indium, aluminum, silicon, and III–V compound semiconductors, minimizing adhesion and contamination during high-temperature processing.
PBN is widely used in MBE (Molecular Beam Epitaxy) systems and crystal growth technologies such as VGF, LEC, and Bridgman methods. PBN crucibles, liners, and evaporation sources provide ultra-clean processing conditions and maintain chemical stability at high temperatures, enabling the growth of high-purity crystals including GaAs, InP, and GaN.
In PVD, evaporation, and MOCVD systems, PBN components such as crucibles, liners, and thermal shields are selected for their low outgassing, excellent vacuum compatibility, and resistance to thermal fatigue. These properties help ensure consistent process conditions and high-quality thin-film deposition.
PBN is commonly used as an electrical insulation material in pyrolytic graphite (PG) vertical heaters and other high-temperature heating assemblies. Its ability to maintain electrical insulation and structural stability at elevated temperatures makes it suitable for demanding semiconductor thermal processes.
Due to its high purity and chemical stability, PBN is frequently used in laboratory crucibles, sample holders, and furnace components for advanced materials research and analytical instrumentation, where contamination-free environments are essential.
The performance of PBN components is closely tied to CVD process control and component design. Factors such as deposition uniformity, wall thickness, and crystal orientation directly influence thermal behavior, mechanical integrity, and service life. As a result, most PBN components are custom-engineered to meet specific application requirements.
With its unique combination of ultra-high purity, thermal stability, chemical inertness, and electrical insulation, Pyrolytic Boron Nitride ceramics serve as a foundational material for advanced semiconductor and high-temperature vacuum technologies. As industry demands continue to move toward cleaner processes and higher thermal performance, PBN remains a reliable and indispensable material solution.